Legislation Free Australian Legal Resources LibGuides at The Australian National University

The Federal Register of Legislation (the Register) is the authorised whole-of-government website for Commonwealth legislation and related documents. It contains the full text and details of the lifecycle of individual laws and the relationships between them. The Register is managed by the Office of Parliamentary Counsel in accordance with the.
P2, R&R S6.1 What is the difference between Common Law and Statute Law? YouTube

The rule of law and the separation of powers limit the powers of the Parliament, the Executive and the Judiciary. The Parliament and the Executive must act lawfully and can be held to account by the courts if they don't. The Australian Parliament cannot judge the limits of its law-making powers—this is the role of the High Court of Australia.
Case Law The Law of Australia Research Guides at Indiana University

The Federal Parliament's legislative powers. A new Commonwealth (national) law can only be made, or an existing law changed or removed, by or under the authority of the Federal Parliament; that is, by or in accordance with an Act of Parliament. Under Australia's Constitution the Federal Parliament can make laws only on certain matters.
Infographics on the rule of law Rule of Law Institute of Australia

1. Legislation begins in draft form as a 'Bill' introduced into Parliament. A Bill is always introduced by a Member of Parliament, who gives a speech describing the intent of the proposed law and why it is necessary. This is called the Second Reading Speech. Bills are often accompanied by Explanatory Materials, which explain in detail what the.
Australia's Craziest Laws Myth or legislation? Nick Xenophon & Co. Lawyers

Geoffrey de Q. Walker, The rule of law: foundation of constitutional democracy, (1st Ed., 1988). The rule of law is the foundation of how Australian society is governed. Individuals in Australia and our governments are bound by and entitled to the benefit of our laws. Australian Government - Attorney-General's Department.
Sexual Assault and Age of Consent Australia Laws Complete Guide NSW Criminal Defence Lawyers

In Australia, the law is made up of two main components: Also known as statute law. These are laws made by government, after debate. This is judge-made law where courts interpret the law and decide cases based on how similar cases have been decided in the past and apply those decisions to the circumstances of the case they are currently deciding.
Australian Law and Order stock image. Image of symbol 42956039

Making a Law. There are three different types of law. Statute Law is the law made by Parliament. It is introduced in a Bill and, if passed, becomes an Act. Common Law is judge-made law, developed through centuries of precedent, or earlier judgements on cases before courts. The Commonwealth and States' Constitutions set out the basic structure.
Overview of the court system in Australia Court Procedure Australia

Australian courts sometimes look to Australia's international treaty obligations when interpreting laws made by Parliament. When there is a gap in the law or uncertainty, they may look to human rights treaties and other international law for guidance.
PPT Statute Law Common Law PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1913869

The Australian statute book as a body of law remains relatively unexplored, despite its importance to Australian society. Visitors to its pages are likely to jump into a selected Act or narrow body of legislation, such as in relation to health insurance or environmental approvals. The DataHub includes the first complete set of public data on.
The Australian Legal System

Statute law, referred to as codified law, is a set of universally accepted regulations that provide guidance and order in a specific society, organization, or country. Its origin derives from the Latin meaning "that which is fixed or settled" - implying that statute law must be adhered to.
15 most bizarre laws in Australia that make no sense

In Australia, statutes of limitations are governed by commonwealth, state and territory legislation. Statutes of limitations in Australia can apply to offences including the following: Criminal offences. Civil offences. Traffic offences. You should also be aware that statutes of limitations vary between different state and territory jurisdictions.
Constitution Rule of Law Education Centre

The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) includes: penalties, enforcement powers and consumer redress options. The ACL applies nationally and in all States and Territories, and to all Australian businesses. For transactions that occurred prior to 1 January 2011, the previous national, State and Territory consumer laws continue to apply.
Types of Law Study Guide Democracy Year 8 LibGuides at St Albans Secondary College
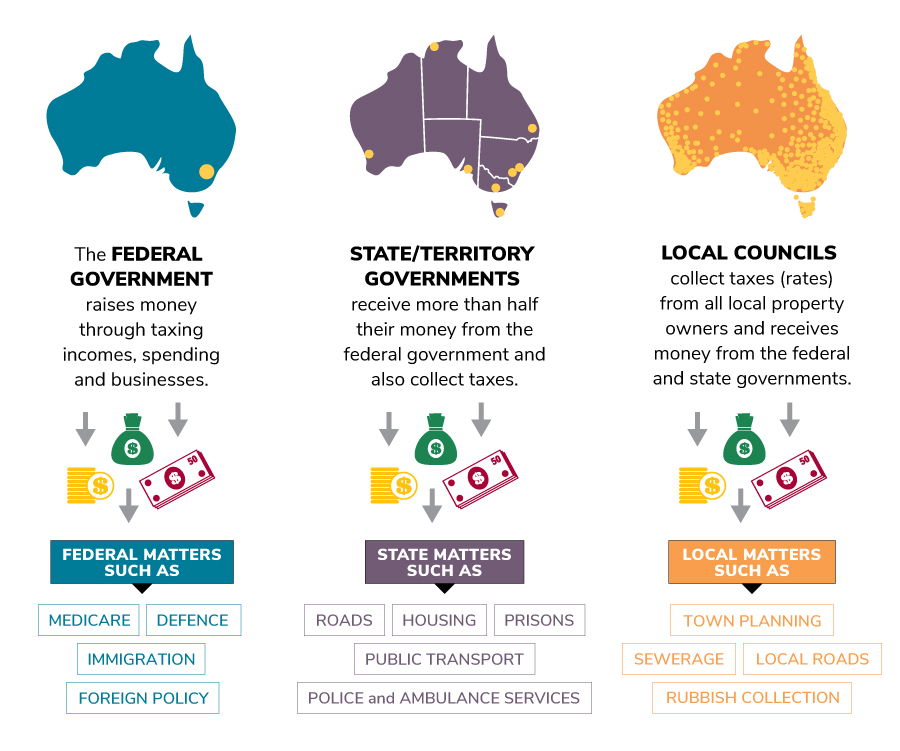
A Q&A guide to the legal system in Australia. The Q&A gives a high-level overview of the key legal concepts including the constitution, system of governance and the general legislative process; the main sources of law; the court structure and hierarchy; the judiciary and its appointment; the general rules of civil and criminal litigation.
WHS Legislation & Regulation Pyramid Australia Safe Design Australia

Law made by Parliament is called statute law or legislation. Statute law is made when Parliament agrees to a bill - a proposal for a new law or a change to an existing one. In the Australian Parliament, a bill becomes a law after it has been passed by a majority vote by the House of Representatives and the Senate and is given Royal Assent.
Understanding the Australian Legal System, 7th Edition by John Carvan, Paperback, 9780455234410

years was the extent to which the common law had been steadily displaced by statute law.9 By McPherson's reckoning, in the period between 1988 and 2006, a period of less than 20 years, the Queensland Parliament had enacted five times more legislation than was enacted in the 135
Easy Guide To Australian Law by Peter Fairfield

Australian statute law is integral to the country's legal structure. It informs citizens about their rights and duties, and renders a platform for the building of legislation. Having knowledge on how this system functions and being adept in its interpretation are significant attributes in understanding the Australian judiciary. This article.
.