Power BI Tips for Star Schema and Dimensional Data Modeling

The Fact table also has foreign keys which refer to candidate keys in the Dimension tables. Going back to our e-commerce example, the Fact table could be Sales, and could include: Quantity_sold (a.
Fact and Dimension In Data Warehouse
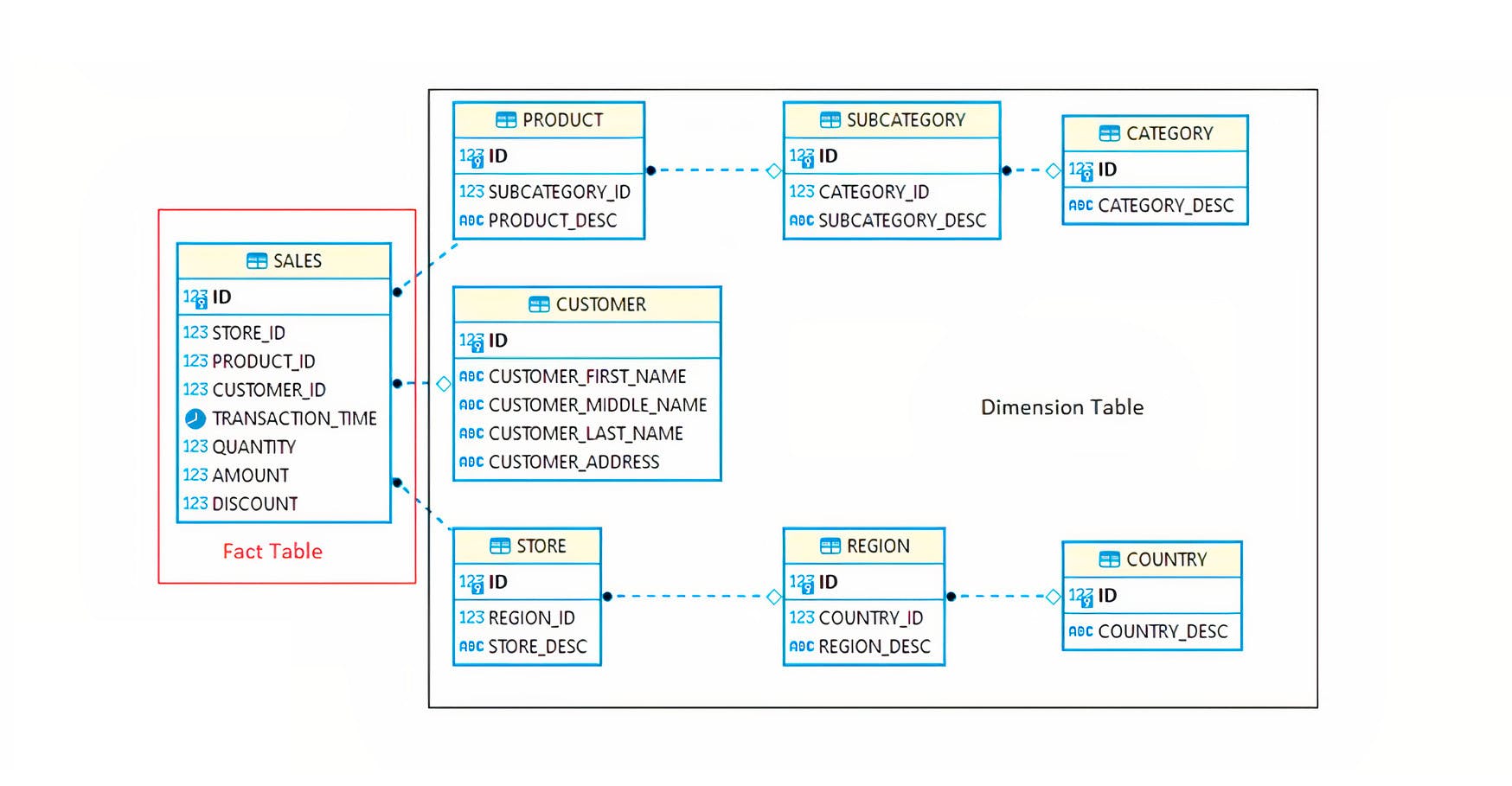
Example: Fact vs Dimension Table . Let us understand the fact and dimension table with certain examples. Suppose there is production of noodles in an industry. Fact table involves organized data on food processing, storage and delivery information. The fact table can be structured like:
Fact table and Dimension table Data Warehousing YouTube
The example I've shown above is a good example of how fact and dimension tables work together to derive key insights that can be suited to specific needs.
Datawarehousing Concepts Basics (Fact and Dimension Table)
The main difference between fact and dimension tables is that a fact table contains quantitative data that can be aggregated, while a dimension table contains descriptive data about the dimensions of your data. For example, a fact table may contain sales figures, while a dimension table may contain information about the products sold.
FACT table, DIMENSION table ,Difference between fact table and dimension table YouTube

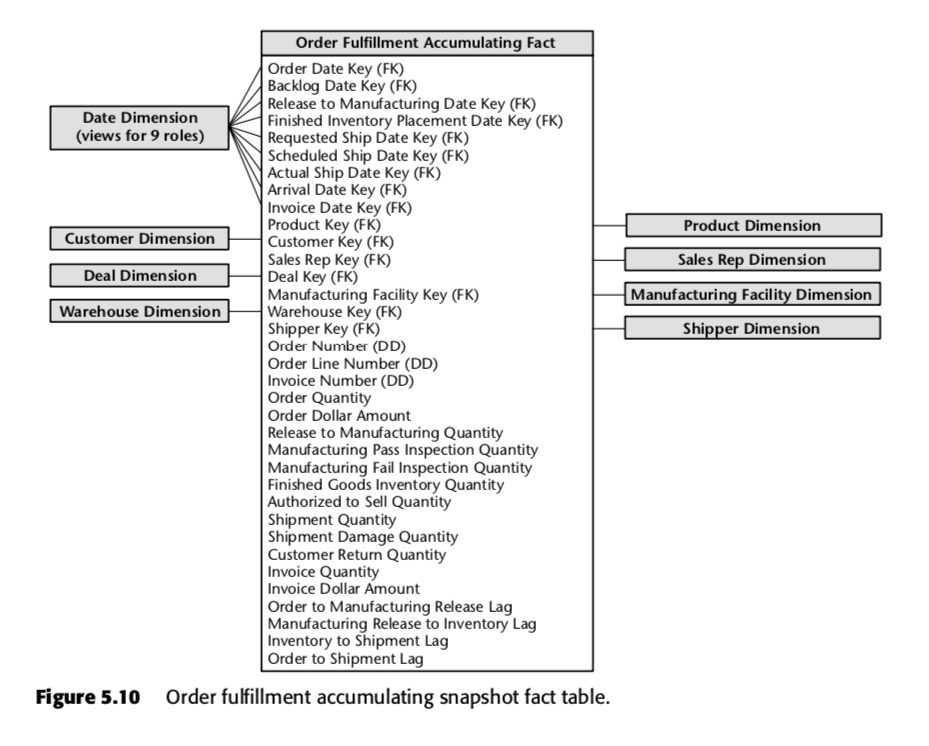
May 7, 2020 . 9 min read. Ralph Kimball's dimensional data modeling defines three types of fact tables. These are: Transaction fact tables. Periodic snapshot tables, and. Accumulating snapshot tables. In this post, we're going to go through each of these types of fact tables, and then reflect on how they've not changed in the years since.
Types Of Fact Tables In Data Warehouse With Examples Elcho Table
A Fact table is a table that keeps numeric data that might be aggregated in the reporting visualizations. A Dimension table is a table that keeps descriptive information that can slice and dice the data of the fact table. The definition above, although correct, can lead to creating heaps of different type of tables and calling those a Dimension.
Difference Between Fact Table and Dimension Table (with Comparison Chart) Tech Differences
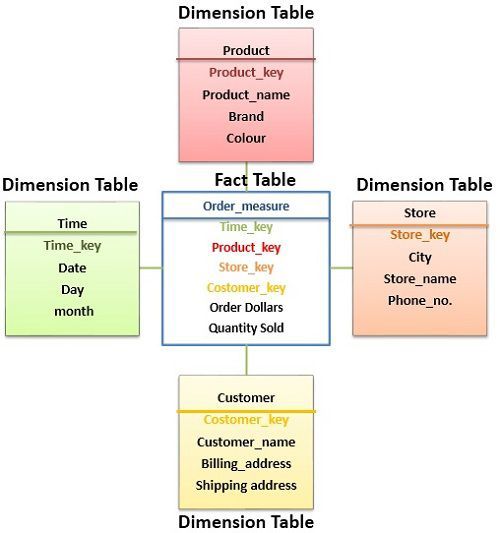
A fact table grows vertically and does not have any hierarchy. Located at the center of the schema, it is defined by data grain. However, a dimension table has more attributes and is a companion to the fact table. The data in the dimension table is only in textual format. It grows horizontally and includes hierarchy.
What Is Factless Fact Table In Data Warehousing With Example Elcho Table

The fact table is located at the center of a star or snowflake schema, whereas the Dimension table is located at the edges of the star or snowflake schema. A fact table is defined by its grain or most atomic level, whereas a Dimension table should be wordy, descriptive, complete, and of assured quality. The fact table helps to store report.
Fact Table and Dimension Table Differences & Examples // Unstop

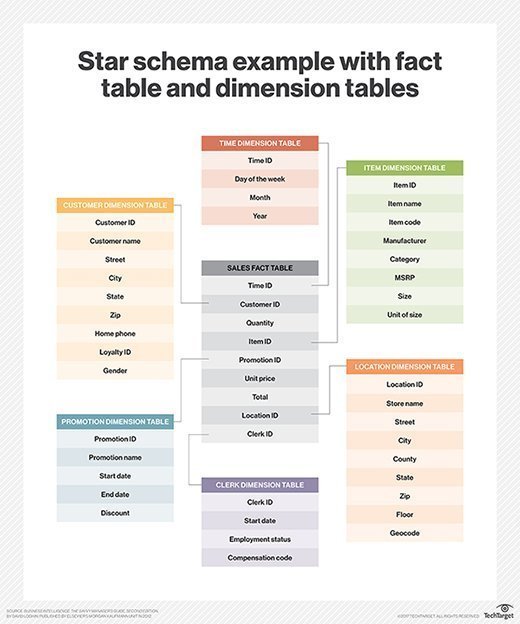
Fact Table vs Dimension Table Star Schema Example. Fact tables usually contain several measures related to the tied attribute dimensions. We may see certain measures on a fact table such as revenue, quantity, amount, etc… A fact table without any measures is known as a "fact-less fact". The relationship between a dimension and fact table.
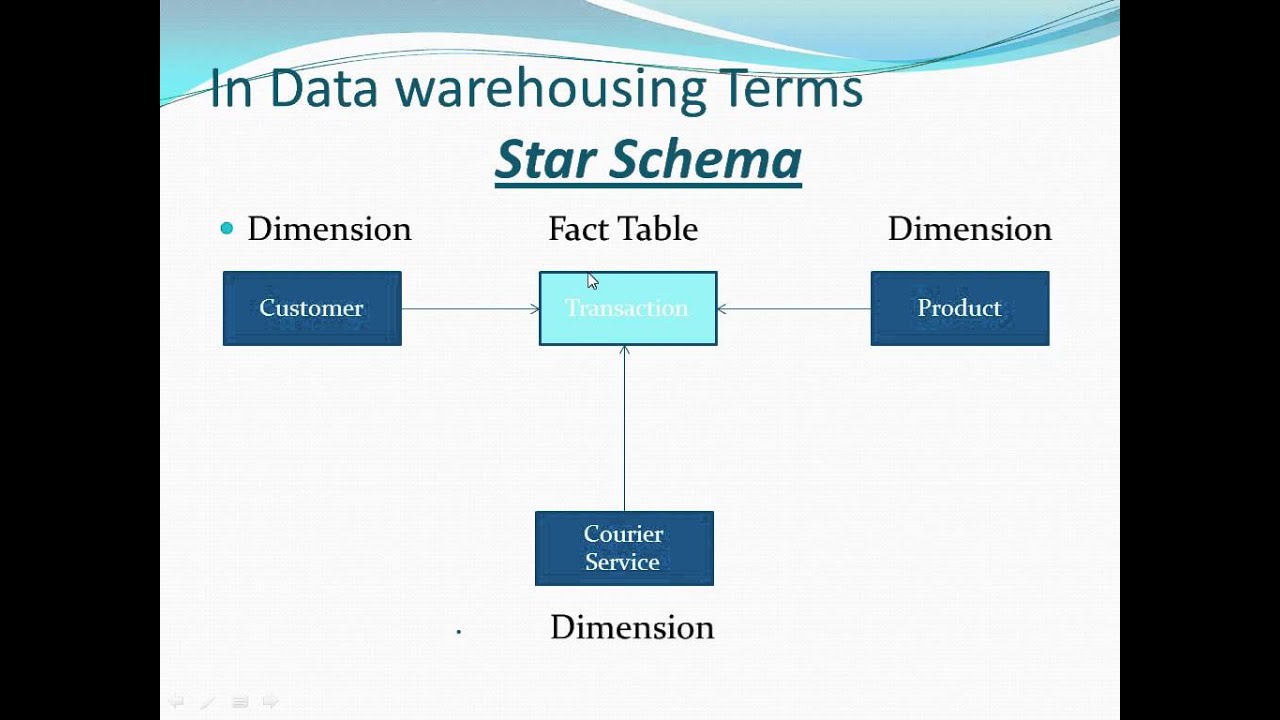
Facts and Dimensions Star (schema) Crossed Lovers The Data School Down Under

A fact table holds primary keys of the referenced dimension tables along with quantitative metrics. A dimension table holds the descriptive information for all fields included in a fact table. We'll discuss their differences in further detail and provide an end-to-end example to demonstrate how these concepts are utilized in real-world projects.
Dimensions and Facts in Terms of Data Warehousing

Step 2: Define granularity for the fact table. In this example, we choose the granularity at the transaction level, where each record represents a single product sold in a transaction. Step 3: Create the fact table with columns for the facts and foreign keys to the dimension tables. Fact table: Sales_Fact.
How to Join a fact and a type 2 dimension (SCD2) table · Start Data Engineering
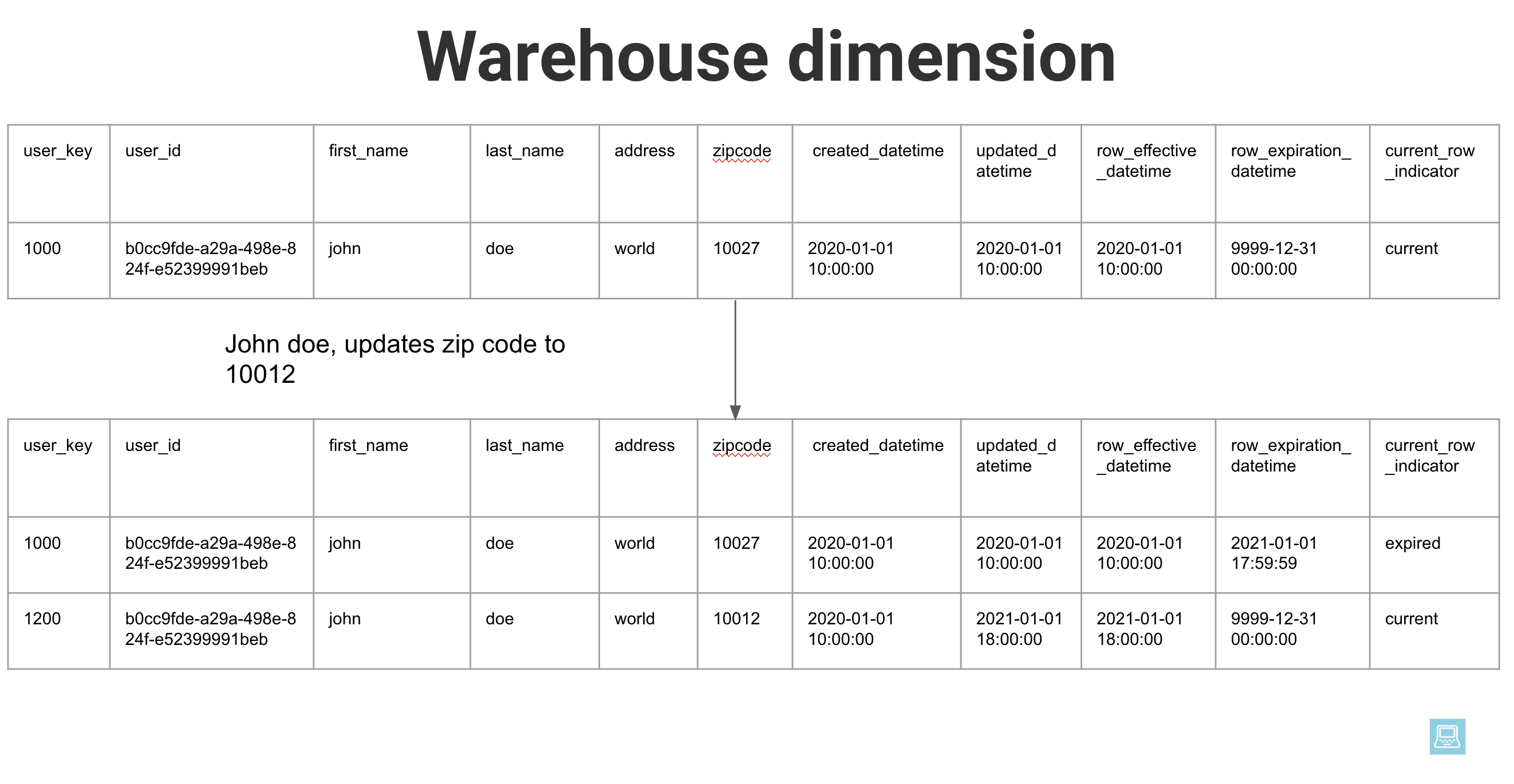
Fact and dimension tables are interdependent. Fact tables include foreign keys that link to primary keys in dimension tables. These relationships enable analysts to associate quantitative data.
Dimension tables vs. fact tables What's the difference? TechTarget
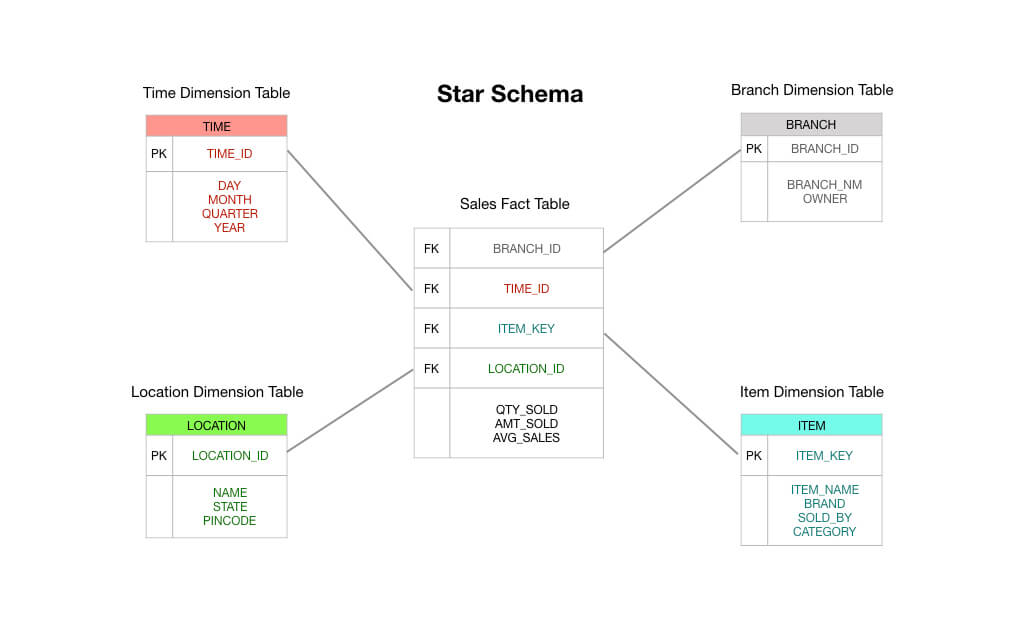
The fact table mainly consists of business facts and foreign keys that refer to primary keys in the dimension tables. A dimension table consists mainly of descriptive attributes that are textual fields. A dimension table contains a surrogate key, natural key, and a set of attributes. On the contrary, a fact table contains a foreign key.
The Three Types of Fact Tables
The Open, High, Low, Close, and Volume columns denote measures on entities that can change over time. A dimension table in a data warehouse model characterizes a column in the fact table as belonging to a dimension value, such as a date or a symbol. The diagram below shows two tables used for storing dimension values.
Dimension Table And Fact Example

The key differences between Fact and Dimension Tables are as follows: The Dimension table is a partner to the fact table and contains descriptive qualities that can be used as query constraints. The fact table includes measurements, metrics, or facts about business operations.
Dimensions and fact tables what is it and how to work with them in Power BI Trainings
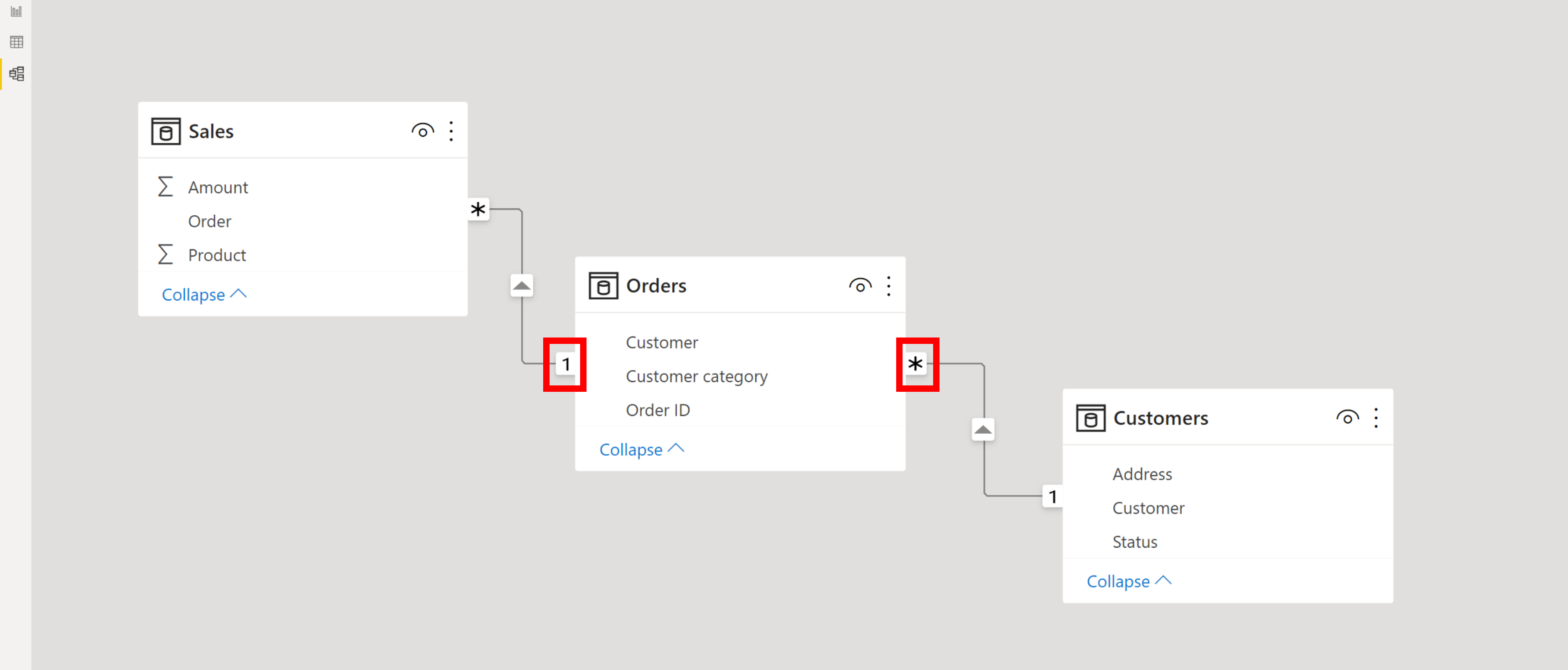
Fact tables and entities also contain foreign keys to the dimension tables. These foreign keys relate each row of data in the fact table to its corresponding dimensions and levels. Fact tables and entities use primary keys that are composite keys. A composite key is made up of a subset of other keys. If a table or entity in a dimensional model.
.